Antibodies, which are also known as an immunoglobulin, are normally secreted by the plasma cells for neutralizing antigens like viruses and bacteria. Representation of antibodies is y-shaped molecules, which are composed of four polypeptides of two heavy and two light chains.
The antibodies can be classified into two important types, which are known as polyclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies.
Production of polyclonal antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies are heterogeneous mixtures, which are produced by the B cell clones within your body. They are capable of recognizing as well as binding to different epitopes of one particular antigen.
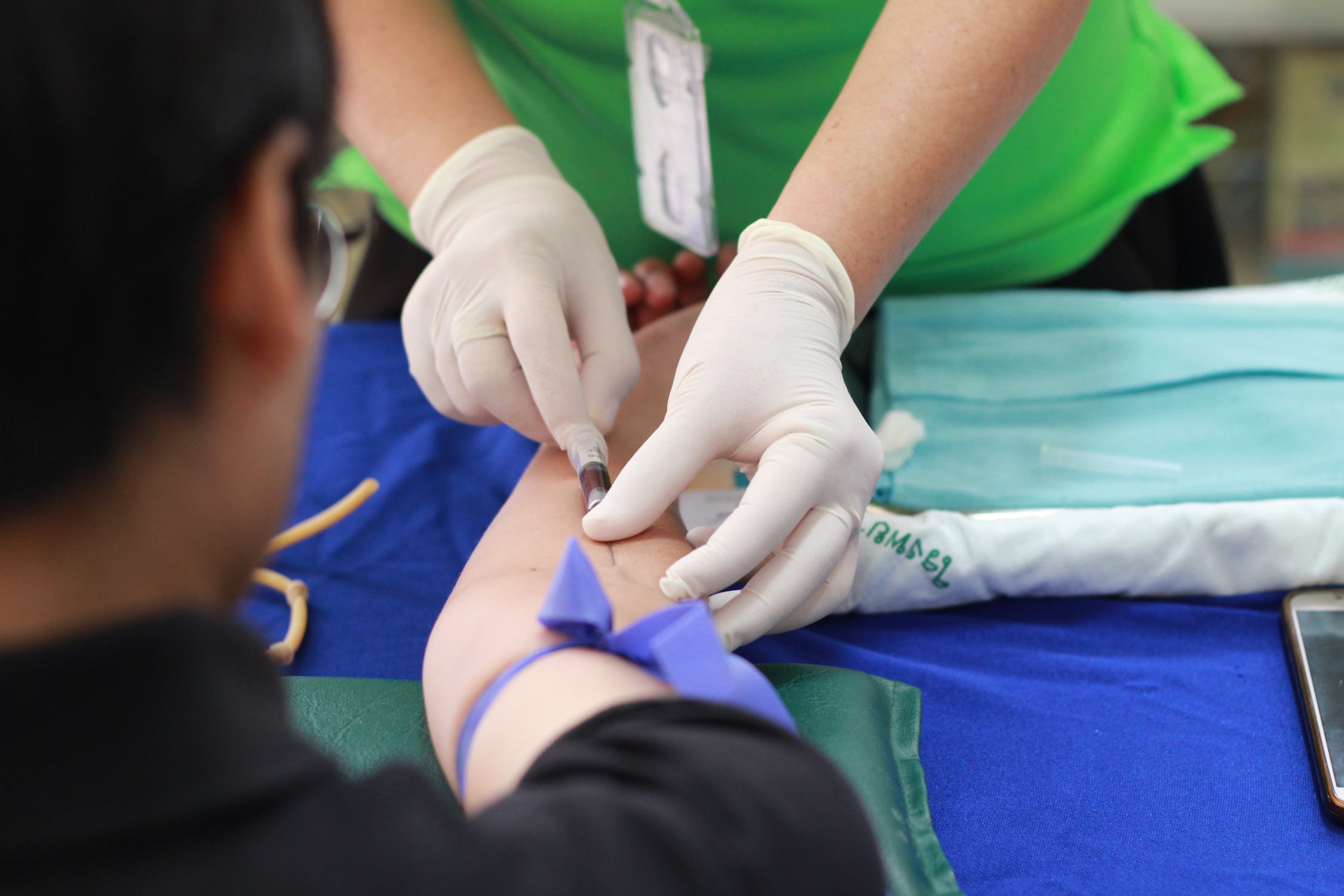
Any polyclonal antibody is normally produced after the immunogen has been injected into animals.
After injecting the animal with specific antigen, secondary even tertiary immunization is also given for producing antibodies against that particular antigen. After the process of immunization, the polyclonal antibodies will be obtained right from the serum.
Advantages of polyclonal antibodies
It is important to understand that polyclonal antibodies have different advantages, which are responsible for making them useful for several applications. Given below is a list of the advantages associated with polyclonal antibodies.
- A short time of production and low cost.
- Stable as well as tolerant of buffer and pH changes.
- Have a high affinity. Since polyclonal antibodies are capable of binding to more than a single epitope, they can help in amplifying signals from target proteins even when the expression level is low. This is why these antibodies are perfect for chromatin immunoprecipitation and immunoprecipitation.
- They are capable of tolerating minor changes in the antigen. The changes include polymorphism, slight denaturation, and heterogeneity of glycosylation.
Disadvantages of polyclonal antibodies
Apart from the several advantages, polyclonal antibodies are also known to have different disadvantages as well. Given below is a list of the disadvantages associated with polyclonal antibodies.
- They are prone to the variability of batches.
- The multiple epitopes are responsible for making it significant for checking the immunogen sequence for cross-reactivities.
Diagnostic studies
Polyclonal antibodies are considered to be perfect regions for several diagnostic assays and hemagglutination reactions because of the ability that they have of recognizing several epitopes of one target molecule.
The ideal use of polyclonal antibodies is detecting unknown antigens. Polyclonal antibodies are normally used as secondary antibodies in microarray assays, western blotting, flow cytometry, Elisa, etc.
The role of polyclonal antibodies is binding to different epitopes and amplifying signals, which lead to better detection. To know more, visit the official website of mybiosource.com
Treatment
Monoclonal antibodies are capable of treating the cancer cells and treating a variety of other diseases, as stated by www.healthcareitnews.com. However, polyclonal antibodies are not capable of treating the cancer cells because they lack specificity and they possess a high degree of cross-reactivity.
Polyclonal antibody therapies can be used for several transplants as well as treating important diseases. However, it is important to understand that polyclonal antibodies are not as capable as monoclonal antibodies.
Conclusion
Polyclonal antibodies are being used in a wide range of assays for the detection and diagnosis of several diseases. You must understand polyclonal antibodies perfectly so that you can understand their functions.
Guest Post Author:-
Walter Moore is a health expert who has been running many health seminars and public discussions. He also manages his blog and reviews the health-related details provided by authentic sources.
- How Primary Care Doctors Are Your First Line of Defense - December 23, 2024
- Live-In Caregiver Jobs: Providing Support, Building Bonds - December 19, 2024
- Caring for Your Porcelain Veneers: Tips for a Lasting Smile - November 12, 2024